Understanding Management Styles: Guide to Effective Leadership
A leadership position isn't a title in your life: It's a chance to make a real impact and a serious responsibility at the same time. Now you can't simply manage…
A leadership position isn’t a title in your life: It’s a chance to make a real impact and a serious responsibility at the same time. Now you can’t simply manage tasks or oversee projects; you should inspire, support, and strategically guide your teams toward long-term success.
You should be ready to motivate employees, build strong relationships with team members, and shape a thriving company culture based on the organization’s values. However, leadership is more than just charisma or authority. It takes emotional intelligence, strategic thinking, and a real understanding of the people you’re leading.
Leaders with strong emotional intelligence create a work environment where 70% (Hay Group) of the climate is positive and team performance is higher. The most successful leaders are those who are flexible, reflective, and intentional about how they manage and communicate.
So, first things first, you need to understand your own management style. That means more than knowing the name of a style or picking one that sounds good. You should explore the different types of management styles, recognize their strengths and weaknesses, and figure out how each one plays out in real-life situations.
The effort will be worth it. According to research, companies that actively train leaders to understand and adapt their management styles see up to a 25% increase in organizational performance.
Let’s examine the most common types of management styles, from autocratic to democratic, transformational to laissez-faire, and beyond. You’ll explore how each style influences decision-making, employee engagement, and team dynamics.
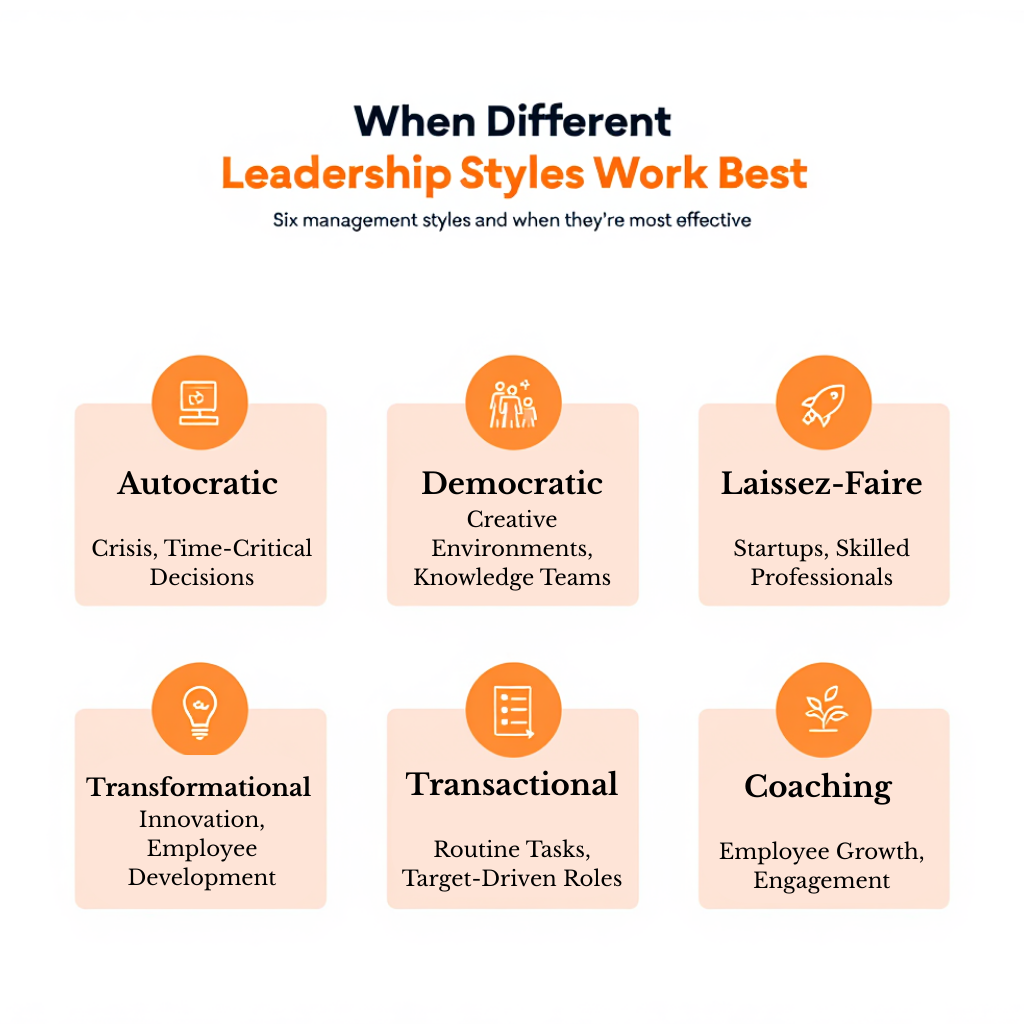
Autocratic Style of Management
The autocratic style of management is based on a highly centralized approach to decision-making. If you choose this management style, it means that you have significant control, make choices, and set direction for your team or company. The emphasis is on top-down communication and a “my way or the highway” mentality.
Distinctive Features of Autocratic Management Style
- Leaders make all decisions.
- Employees make minimal input.
- There’s a strict hierarchical structure.
- All communication is directive.
- Processes and outcomes are under control.
- Speed and adherence to rules are crucial.
- The system functions on punishment and reward.
Why Autocratic Management Style Works
- Decisions are made very quickly.
- Team members receive unambiguous instructions, which reduces misinterpretation.
- You hold clear responsibility for outcomes, as all decisions originate from you.
- Tight control over processes and outcomes can be effective in high-risk environments.
Why Autocratic Management Style Can Be a Problem
- Lack of idea sharing stifles creativity and limits innovation.
- Lack of autonomy lowers morale, engagement, and job satisfaction.
- Reliance on one leader creates risks if they fail or are absent.
- An autocratic style drives higher turnover as employees seek empowerment.
When Autocratic Management Style is Especially Effective
An autocratic leadership style is more rigid or oppressive than others. However, it can be vital in situations where speed, precision, or uniformity matter more than collaboration or creativity. Let’s find out where this style can make the difference between success and failure.
Crisis Situations
In crises, fast, unilateral decision-making can save a company. A great example is the Tylenol Crisis (Time). Several people died after cyanide was found in Johnson & Johnson capsules. CEO James Burke had no time for lengthy consultation, and he made an immediate autocratic decision to pull 31 million items nationwide at a cost of $100M.
This decisive action restored consumer trust and is now considered a gold standard in crisis management.
Dangerous Spheres
Leaders of industries where errors can cause disasters usually rely on an autocratic style of management. At Toyota, if a defect appears, the whole line can be stopped (the andon system), but managers decide how it’s fixed. This strict, top-down discipline helped Toyota build its reputation for reliability.
Inexperienced Teams
When employees lack skills, a directive style helps them avoid mistakes. At Foxconn, many workers are young and unskilled, which is why management uses strict rules and close supervision. This tough system enables Apple products to be made at a massive scale with consistent quality.
When Time is Critical
Autocratic decision-making can help you to accelerate innovation when timing is critical. CEO Albert Bourla ordered teams to skip normal steps and run trials in parallel, investing billions upfront. This top-down decision let Pfizer deliver the first COVID-19 vaccine in under a year (New York Times).
Consistency in Franchises and Scaling
Uniformity across thousands of outlets requires strict top-down control. If you run a franchise, an autocratic style ensures consistency across all locations.
Ray Kroc set strict rules for cooking, portion sizes, and service. Franchisees couldn’t improvise, which guaranteed that a Big Mac tasted the same everywhere — a key to McDonald’s global success.
Tactics and Techniques of Autocratic Style
If you want to keep tight control and ensure consistency, these things can help you lead decisively:
Direct Command
You need to give instructions that are clear, specific, and non-negotiable. Don’t leave room for guesswork — your team should know exactly what needs to be done and how. This prevents confusion and keeps everyone on the same page.
Close Supervision
You should maintain constant oversight of tasks to catch mistakes early and make sure standards are met. It’s essential for high-stakes or high-speed operations.
Standard Operating Procedures
You must establish and enforce detailed procedures for all tasks. They ensure that every team member works consistently, whether it’s a factory line, a restaurant franchise, or a complex project.
Performance Monitoring
You should implement strict monitoring systems to track task completion and adherence to directives. Digital dashboards help you see instantly who’s on track and who needs guidance.
Limited Delegation
You can delegate tasks, but only those that are clearly defined and low-risk. This ensures quality and reduces the chance of errors.
Democratic Management Style
The democratic style of management, also known as participative leadership, centers around inclusive decision-making where all your team members actively contribute insights and ideas.
Distinctive Features of Democratic Management Style
- You, as a leader, value input from your team.
- Decisions are a collaborative process, though final responsibility is on you.
- Horizontal communication (bottom-up and top-down) prevails.
- Emphasis is placed on transparency, trust, and shared accountability.
- Everyone is encouraged to be creative and to use discussion-based problem-solving.
Why Democratic Management Style Works
- You get higher job satisfaction and commitment from your team. They feel valued, boosting loyalty and reducing turnover, because for 70% of employees, their work defines their sense of meaning and purpose (McKinsey).
- Open discussion leads to more creative ideas and better solutions.
- You have stronger team cohesion and trust because the team feels a shared sense of purpose.
- You get better decision-making quality due to diverse perspectives.
Why Democratic Management Style Can Be a Problem
- Slow decision-making due to you need to gather input from many sources.
- Potential for conflict and superficial consensus.
- When decisions are shared, responsibility may become blurred.
- Democratic leadership works best with skilled, engaged teams. Otherwise, decision quality may suffer.
When Democracy Is Especially Effective
Democratic leadership in particular contexts can be a powerful factor for performance and innovation. Its strength is in strong collective intelligence, encouraging participation, and creating an atmosphere of shared responsibility. Let’s consider several situations where this leadership style proves especially effective.
Creative Environments
In industries where innovation thrives on diverse ideas, democratic leadership accelerates creativity and problem-solving.
For example, 3M established its “15% culture”, allowing engineers and researchers to dedicate up to 15% of their work time to personal, passion-driven projects. This environment of autonomy and creative freedom led to the invention of the now-iconic Post-it Notes and many other innovations.
Employee Ownership
When employees have a stake in the company through ownership or profit-sharing, democratic leadership fosters engagement, accountability, and long-term commitment. Workers who feel a sense of ownership are more likely to contribute ideas, collaborate, and drive performance.
Knowledge-Intensive Teams
Software development, scientific research, and consulting firms benefit from structures where team members can propose solutions, challenge assumptions, and iterate collectively. This leads to more robust, well-rounded decisions and innovation.
Organizational Change and Transformation
During times of major change—mergers, restructuring, or cultural transformation—democratic leadership helps gain buy-in from employees at all levels. By including staff in decision-making, companies reduce resistance, increase transparency, and foster a sense of shared purpose.
Tactics and Techniques of a Democratic Style
If you want to listen to the perspectives of your team and individual experts, give them room for innovation, and help them feel part of a larger mission, the following points will be useful to you.
Structured Input Sessions
Plan specific moments for team input, such as brainstorming in meetings, then decide efficiently.
Set Boundaries
Clarify what decisions are collaborative and which are leader-driven to maintain clarity.
Use Hybrid Models
Adopt democratic decision-making where it adds value, and switch to autocratic or hybrid styles when speed or clarity is critical.
Maintain Transparent Communication
Share decision rationales openly and regularly. Appreciate and recognize your team’s contributions.
Laissez-Faire (Delegative) Management Style
Choosing this style means you step back, trust your team to self-manage, and intervene only when necessary. Communication flows laterally rather than top-down, fostering autonomy and ownership.
Distinctive Features of Laissez-Faire Management Style
- You provide minimal direct control.
- There are high levels of employee autonomy and decision-making.
- Managers serve as supporters and resources.
- You rarely intervene unless support is requested.
- Emphasis is on trust, flexibility, and creativity.
Why Laissez-Faire Management Style Works
- It fosters innovation and creativity for passionate, highly skilled employees.
- High-performing and experienced teams can self-direct and may produce exceptional outcomes without micromanagement.
- It helps boost job satisfaction and retention.
- Organizations with non-hierarchical structures have stronger resilience in the long term.
Why Laissez-Faire Management Style Can Be a Problem
- Such an approach can create ambiguity and low role clarity.
- You risk getting poor performance with inexperienced teams.
- There’s potential for disengagement of your team or some members.
When Laissez-Faire Is Especially Effective
A laissez-faire leadership’s effectiveness depends largely on the maturity of the team, the clarity of goals, and the type of work being done. There are several cases where this leadership approach shines most.
Startups and Fast-Moving Environments
Startups must adapt quickly, try new ideas, and make changes without being slowed down by bureaucracy. Laissez-faire leadership gives teams the freedom to act and encourages innovation.
Highly Skilled Professionals and Innovators
Experts with deep domain knowledge thrive when you trust them. This style reaches the full potential of your team. For example, Pixar fosters a culture of creative freedom; its animators and artists develop ideas independently. This hands-off environment has led to blockbuster successes such as Toy Story, Finding Nemo, and Up (HBR).
Tactics and Techniques of a Laissez-Faire Style
To lead effectively while stepping back, consider these practices.
Set Clear Goals and Expectations
Establish measurable milestones, clarify desired outcomes, and make expectations transparent for your team. This creates a shared sense of direction without constant supervision.
Provide Support without Micromanaging
Be available for consultation and training when needed. You can also arrange periodic knowledge-sharing sessions, where the team learns from one another.
Clarify Accountability Paths
Define who is responsible for outcomes, even when roles are flexible, to maintain accountability. A laissez-faire approach can blur responsibilities if left unchecked, so it’s important to establish ownership for each deliverable. This not only keeps projects on track but also prevents conflicts or overlaps in duties.
Foster a Trusting Culture
Build confidence in your team’s capabilities. Trust motivates people to take initiative and strengthens collaboration. You should also model trustworthiness yourself: keep your commitments, be transparent, and respect individual contributions.
Monitor Subtly and Intervene Smartly
Digital tools can provide visibility into progress while allowing employees to work independently. If there are issues, you should intervene considerately: offer solutions or redirect efforts without imposing strict control. The goal is to correct course when necessary while maintaining the team’s sense of ownership.
Transformational Management Style
As a leader with a transformational style of management, you should focus on inspiring and motivating employees to achieve results. Emphasize positive organizational culture, trust-building, and empowerment, enabling your teams to exceed expectations.
Distinctive Features of Transformational Management Style
- You spread a compelling vision that gives purpose and direction to your team.
- You encourage creativity and drive innovation.
- There’s individualized consideration with support and mentorship to develop each employee’s potential.
- Leading by example gives an inspirational push forward.
Why Transformational Management Style Works
- Organizations with transformational leaders have up to a 25–50% increase in employee engagement (PMC).
- Employees under transformational leadership show higher satisfaction and commitment.
- Teams are more likely to generate creative solutions.
- A culture of empowerment reduces employee turnover and increases retention.
Why Transformational Management Style Can Be a Problem
- High expectations and constant striving for improvement can stress employees.
- It requires alignment and consistency across all organizational levels to be effective.
- Success depends on the leader’s ability to communicate and embody their vision.
When Transformational Leadership Is Especially Effective
Transformational leadership is a powerful approach that inspires people to go beyond routine tasks and set bigger goals. It is especially valuable where adaptability, creativity, and personal growth are critical.
Organizational Change
During major transformations, transformational leaders help teams navigate change, motivate employees.
Innovation Sectors
This style fosters creative thinking and calculated risk-taking, leading to new products and services.
Developing Employees
Provide individualized mentorship and support to help employees grow professionally and personally.
Tactics and Techniques of a Transformational Style
To lead effectively, consider these practices:
- Communicate a clear vision. Make sure everyone understands the organizational goals and their role in achieving them.
- Foster open communication. Create a safe space for sharing ideas and feedback.
- Invest in development. Offer training and mentorship opportunities.
- Recognize achievements. Reward and acknowledge individual and team contributions to reinforce desired behaviors.
Transactional Management Style
As a leader with a transactional style of management, you emphasize structured tasks, clear expectations, and a system of rewards and punishments. The main focus is on maintaining routine and efficiency, ensuring that employees meet predefined standards and objectives.
Distinctive Features of Transactional Management Style
- You have clear expectations through awareness of roles and responsibilities.
- Performance is directly linked to rewards or punishments.
- Emphasis is on rules, procedures, and established workflows.
- Focus is on achieving specific, measurable objectives within a set timeframe.
- Leaders actively supervise and intervene.
- Creativity is often constrained to maintain consistency and control.
Why Transactional Management Style Works
- Efficiency is in routine tasks.
- Employees understand what is expected and how they will be evaluated.
- Identification of issues happens fast.
- Motivation is through rewards.
- You maintain order and predictability in day-to-day activities.
Why Transactional Management Style Can Be a Problem
- The focus on routine can suppress innovative thinking.
- Constant monitoring and a strict reward-punishment system may lead to decreased job satisfaction.
- Emphasis on immediate goals may overlook long-term strategic planning.
- High pressure to meet targets can lead to stress and turnover.
When Transactional Management Is Especially Effective
Transactional leadership emphasizes order, discipline, and results. This approach tends to work best when tasks are straightforward, processes are repeatable, and performance can be directly connected with rewards or consequences.
Crisis Situations
In high-pressure scenarios requiring quick decision-making, transactional leadership can provide the necessary structure and clarity. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, companies with clear protocols and performance expectations were able to adapt rapidly to changing circumstances.
Manufacturing and Production
Industries with standardized processes benefit from transactional leadership, ensuring that quality and efficiency standards are consistently met.
Sales and Target-Driven Roles
Sales teams often thrive under transactional leadership due to the clear link between performance and rewards. Setting specific sales targets and offering bonuses for achievement can drive motivation and results.
Tactics and Techniques of a Transactional Style
To implement a transactional management style effectively:
- Set clear goals. Define specific, measurable objectives for employees to achieve.
- Establish standard operating procedures. Develop detailed guidelines to ensure consistency and efficiency.
- Implement performance monitoring systems. Use tools to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Provide regular feedback. Offer constructive criticism and acknowledge achievements promptly.
- Maintain a reward and punishment system. Ensure that employees understand the reward and punishment system.
Coaching Leadership Style
A leader with the coaching leadership style focuses on nurturing the personal and professional growth of team members. Coaching leaders act as mentors, guiding individuals to unlock their potential through active listening, constructive feedback, and goal-setting.
Distinctive Features of Coaching Leadership Style
- You understand team members’ perspectives, challenges, and aspirations.
- There’s a high level of leaders’ empathy and emotional Intelligence.
- Leaders collaborate with team members to set and achieve personal and professional goals.
- Regular, actionable feedback is provided to help individuals improve and grow.
- Initiative and ownership of the work are encouraged.
- Continuous learning works for both leaders and team members.
Why Coaching Leadership Style Works
- Employees feel valued and supported, leading to increased motivation and job satisfaction.
- With clear goals and regular feedback, individuals can enhance their skills and productivity.
- Open communication and mutual respect foster a collaborative and supportive team environment.
- A culture of leadership is developed at all levels.
Why Coaching Leadership Style Can Be a Problem
- Individualized attention and feedback require significant time and effort from you.
- Effective coaching demands leaders with strong interpersonal skills and emotional intelligence.
- Employees may become dependent on continuous guidance.
When Coaching Leadership is Especially Effective
Coaching leadership is not equally impactful in every context. However, there are situations where this style proves especially powerful, bringing out the best in individuals and teams.
Employee Development and Retention
When you help employees develop their skills and remain engaged, it strengthens loyalty and reduces turnover. Thus, Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, changed the company’s culture. He encouraged employees to try new things, learn from mistakes, which led to more engagement and innovation (Microsoft).
Complex Problem-Solving and Innovation
Instead of imposing solutions, you guide teams to develop their own ideas, which encourages innovative approaches.
Junior Teams
When employees are new or less experienced, coaching leadership helps them learn and grow. You should guide, provide feedback, and support. But don’t mistake it with dictating every step.
Building a Collaborative Culture
Coaching is especially effective in organizations that rely on collaboration and teamwork. Open communication and encouraging self-directed problem-solving cultivate trust and psychological safety.
Tactics and Techniques of a Coaching Leadership Style
If your goal is to develop talent, improve engagement, and encourage innovation, these approaches are critical:
Active Listening
You must fully understand employee perspectives, aspirations, and concerns. Ask open-ended questions and listen more than you speak. This ensures employees feel valued and heard.
Constructive Feedback
Provide feedback regularly. Frame feedback to highlight learning opportunities and growth.
Goal Alignment and Development Plans
Collaborate with employees to set achievable personal and professional goals. Create development plans and support employees in tracking their progress.
Encourage Autonomy
Give employees the freedom to make decisions within their scope.
Mentorship and Skill-Building
Invest time in training and mentoring sessions. Provide resources for learning and create opportunities for employees to practice new skills.
Regular Reflection
Encourage employees to reflect on their work, challenges, and achievements. Reflection sessions foster self-awareness and continuous improvement.
Art of Adaptability in Leadership
We’ve explored six leadership styles, but let’s be honest — picking just one is not the answer. No single leadership style is universally superior. The most successful managers possess the agility to pivot between different styles based on the context, the individuals involved, and the desired outcomes.
You should develop a nuanced understanding of when and how to apply each approach. When you find your own management style based on existing ones, you can correctly motivate your team and build a strong, resilient team or organization.
FAQ
What is the management style?
Management style is how you lead your team. It’s about how you make decisions, communicate, motivate people, and guide work.
What is the most effective management style?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. The best leaders can switch styles depending on the situation, the team, and the goals. Some situations call for strict control, others for collaboration or creativity. Flexibility is key.
How do I find my own management style?
Explore different styles, their strengths and weaknesses, and see how you naturally lead. Then, practice adapting to situations and team needs.
Can one style work for everything?
No. No single style is perfect. The best leaders mix and match approaches depending on context, people, and outcomes.
How does leadership affect employees?
Leadership shapes engagement, morale, and performance. You can motivate, build trust, encourage growth, and create a positive culture.
Facing similar challenges?
We turn complex technical concepts into clear business value.
Book a Discovery Call
Liubov Nazukina
CMO
Technical writer turned content strategist. Specializes in B2B SaaS, Legacy Modernization, and Automotive Logistics.
Related Articles
8 Key Reasons Why Your Business Needs a Content Strategy
78% of CMOs consider custom content as the future of marketing. Why? First, nearly 74% of companies recognize content marketing as effective for lead generation…
Best E-commerce Strategies: Guide to Success in 2025
In recent years, e-commerce has become an essential component of global retail. Consumers worldwide now enjoy the edges of online purchases. There are over five…
Read Next
7 Essential Leadership Skills for Chief Executives and Practical Tips for Success
A chief executive (CEO) is a person who can lead a company to the top of the market. At the same time, they can ruin it by inappropriate management. This role c…
B2B Content Marketing Trends for 2025-2026: What to Expect and How to Stay Ahead
These days, nearly half of marketers plan to increase their spending on B2B content marketing year over year. You might get surprised, but B2B marketers use mor…